 In order to operate at its best and last a long time, a computer has to be in good health. But what are 4 things a computer must have? PCs don’t need much maintenance, other than a reliable power source. To perform well, PCs use strong and resilient parts that, if destroyed, might jeopardize them and cause a variety of issues. Users of desktop and laptop computers should take the time to get knowledgeable about the internal hardware that powers their machines.
In order to operate at its best and last a long time, a computer has to be in good health. But what are 4 things a computer must have? PCs don’t need much maintenance, other than a reliable power source. To perform well, PCs use strong and resilient parts that, if destroyed, might jeopardize them and cause a variety of issues. Users of desktop and laptop computers should take the time to get knowledgeable about the internal hardware that powers their machines.
With enough information, you may quickly determine the most likely causes of your PC’s slowdown and fix them yourself, saving both time and money by avoiding the need to visit a local computer shop. To keep your PC functioning well and allow you to continue using it without interruption, routine maintenance and periodic upgrades are a need. After prolonged use, electrical components deteriorate; this also applies to computer hardware. PCs might slow down for a variety of reasons, but for the most part, you can fix it without touching any sensitive hardware. Having said that, an upgrade is frequently the best option for more serious problems.
What are 4 things a computer must have?
1. Motherboard
The motherboard is the main circuit board that secures all the hardware in place. It is always listed first in a comprehensive list of computer components. From specialized workstations to personal notebooks, every PC has one. A sturdy motherboard has numerous spaces for adding different computer parts, such as RAM and graphics cards. For customizable desktops, motherboards come in a variety of form factors. This includes generic specifications encompassing circuitry arrangement, overall size, number of ports, and more. Only specified motherboard models can fit into various computer cases/chassis.
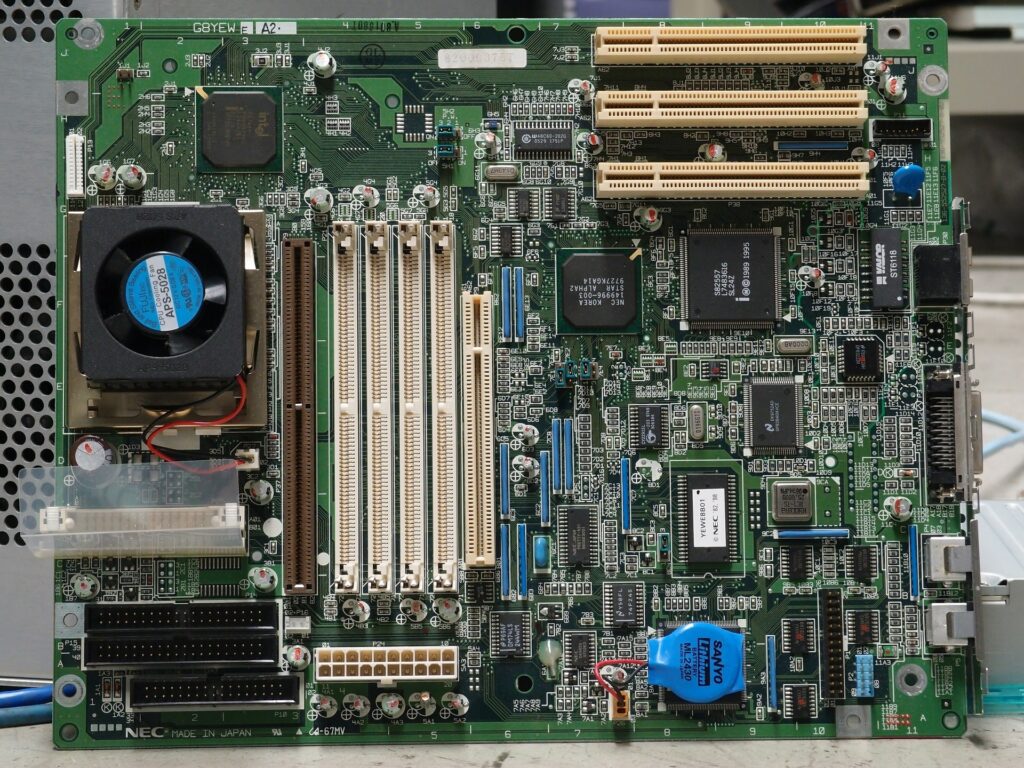

Instead, laptops use specialized motherboards. This means most of their built-in hardware is already soldered onto the appropriate circuits. Only a few components, such as the RAM and storage, can undergo changes. This is due to the laptop’s smaller frame and lighter construction. PCs stop operating properly when a motherboard receives damage. Because of the intricate wiring and electronics in place, a defective motherboard can immediately render your computer unusable and even endanger other components. While desktop motherboards can be easily replaced, this is not true of laptop motherboards, necessitating the purchase of a brand-new laptop.
2. Central Processing Unit (CPU)
Your computer’s ‘brain’ is commonly known as the central processing unit (CPU), sometimes known as the processor. When your computer runs programs or applications, the CPU handles all the complex algorithms and programming. Nowadays, practically all processors include several CPUs to achieve faster processing rates. This results in speedier response times when using applications or accessing the internet. These unique processors are multi-core processors, with 1 processing core assigned to each CPU.
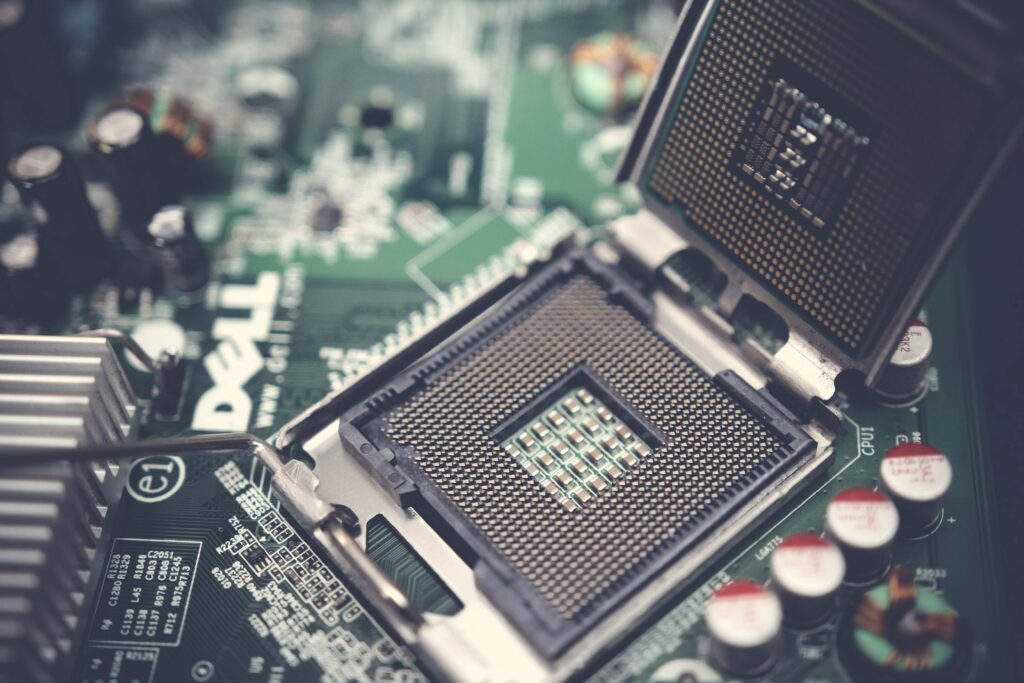
For instance, the top-of-the-line Intel® CoreTM i7-12850HX processor has 16 separate cores. All of these cores collaborate to perform computational tasks, enabling you to complete work that requires a lot of program execution without overtaxing your computer. By overclocking your CPUs, you can gain a little performance improvement by wringing out extra power from them. However, there are dangers associated with this that could harm your CPU, so be aware of that. Remember that even if other components of a PC are operating normally, the processor cannot.
3. Graphical Processing Unit (GPU)
The computer hardware that handles advanced imaging and graphical processes is the graphics processing unit (GPU). A GPU is necessary for your computer to interpret and replicate graphic effects and representations. It is a critical component today because complex images which are nearly always present in today’s media. Particularly in high-end laptops that emphasize lightweight portability and usability, certain top-spec CPUs can also include basic GPUs. The best GPUs, however, are mostly utilized for video gaming. They can handle huge 3D graphics loads while still maintaining smooth frame rates and lag-free experiences.
The CPU and GPU cooperate when playing games. While the CPU oversees the software that runs in the background, such as data and in-game statistics, the GPU handles the heavy lifting in terms of the on-screen graphics and quality. A malfunctioning GPU can cause a variety of issues, including the dreaded “black screen of death.” Losing your GPU would be a nightmare due to the present situation of GPU chip shortages.
4. Random Access Memory (RAM)
Computers use different types of memory to store information and data, with random-access memory (RAM) receiving the most attention. When a program or app opens, a RAM device rapidly loads stored, critical, and currently utilized data and codes that are on standby. Since RAM is a volatile sort of memory, all data is reset when the computer shuts down. This enables the device to swiftly assimilate fresh data during the subsequent session, speeding up loading times.
Almost all commonplace computers, including tiny laptops, can get upgrades with extra RAM. You can do this by purchasing a better RAM device, or RAM stick, that offers more storage space. However, based on your computer activities, you might not use all of the RAM, therefore you should be aware of the optimal amount of RAM for your PC based on its principal purpose (work, gaming, etc.). A broken RAM stick won’t necessarily stop your computer from functioning properly, but it will slow it down over time and cause problems. These can be software crashes, unexpected RAM loss, and boot failure, among others.
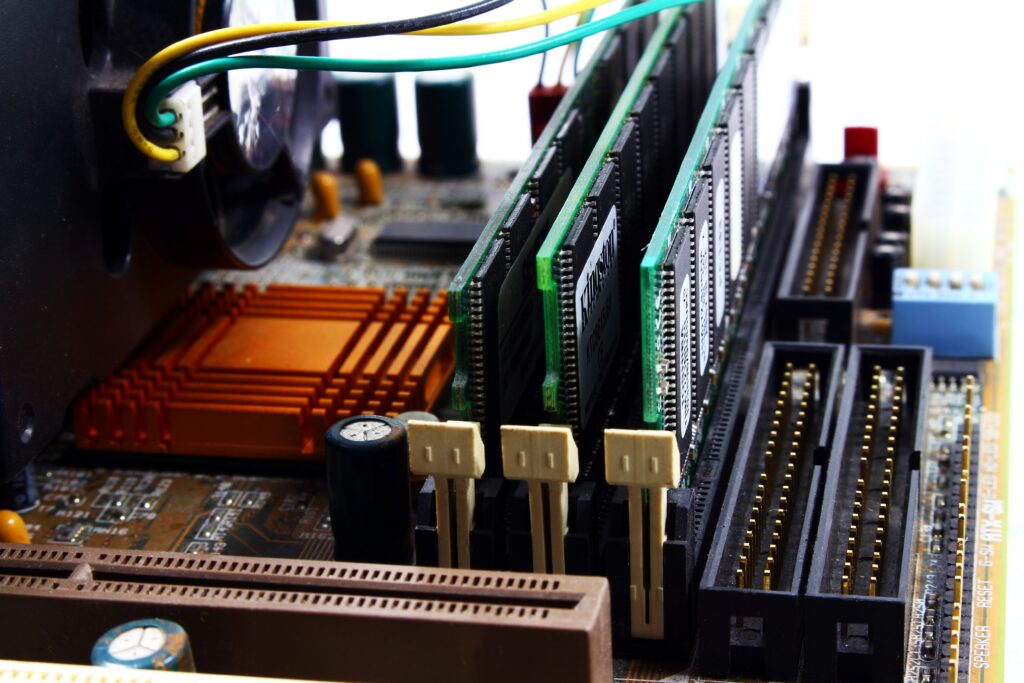
Other Computer Must-Haves
Storage device
A storage device provides the RAM needed to save files and install programs. In contrast to RAM, a storage device’s data gets protection from non-volatile memory. This means that information is permanently preserved in the device’s memory bank and will persist even after you power off the computer (unless manually erased or uninstalled). Internal storage devices in PCs typically come in two flavors: hard disk drives (HDDs) and solid-state drives (SDDs).
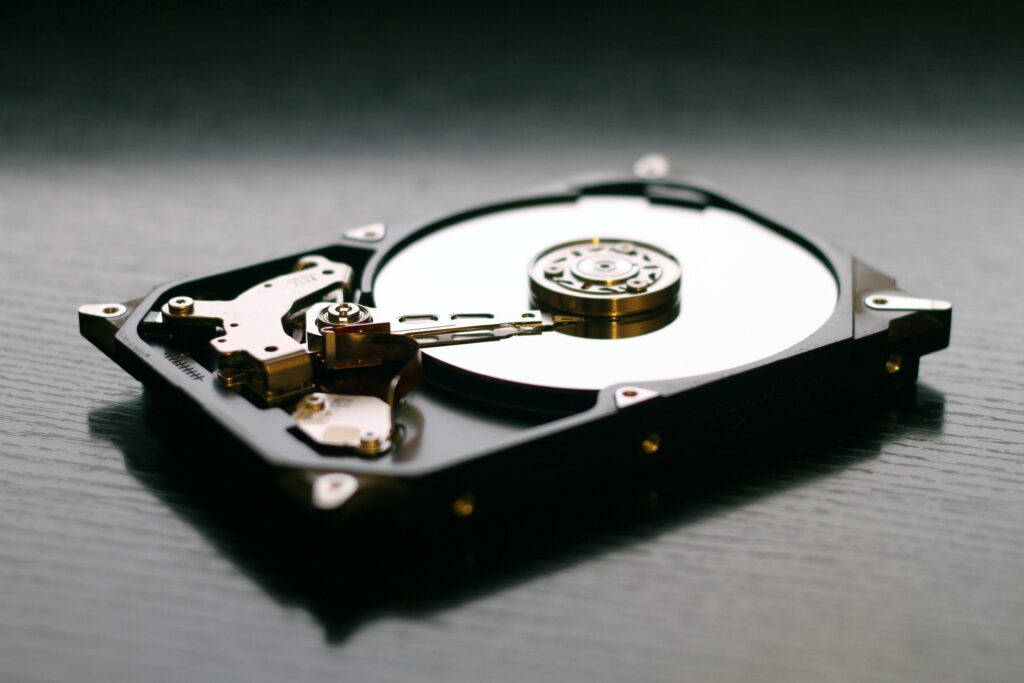

While SDDs are their superior counterparts but cost more, HDDs are the less expensive option but have slower transfer speeds. Dedicated SATA cables connect these devices to your computer, while SAS cables are for large servers and workstations.
There are other supplementary storage options, like portable HDDs and USB flash drives. However, these add-ons are not included in computers. Depending on the specifications, they are instead connected to the PC through various methods. This includes USB ports or external disk drives. Although storage media have little bearing on how your computer boots up, apps that run at startup, such as Microsoft Word or Google Chrome, load directly from your HDD or SDD. Therefore, a damaged storage device might stop everything in its tracks and perhaps ruin your contents. If so, you must replace your hard disk right away, which may need a cumbersome system reformat or Windows reinstall.
FAQs
How many parts does a computer have?
A computer is a sophisticated machine made up of multiple crucial components that collaborate to carry out various functions. A computer can be roughly divided into two categories: hardware and software. The term “hardware” refers to all the actual physical parts of a computer. This would refer to the CPU, motherboard, memory modules, RAM, storage drives (such as hard disk drives or solid-state drives), GPU, and peripherals like the monitor, keyboard, and mouse.
These parts work together to conduct computations and carry out commands. Contrarily, software refers to the immaterial programs, applications, and operating systems in a computer. They provide the hardware with the instructions it needs to follow. The software also enables user interaction and the effective completion of a variety of activities.
What is computer hardware?
Internal components and external peripherals are the two primary categories of computer hardware. The motherboard, CPU, RAM, and other internal components make up the computer’s central processing unit. Together, these parts process data and carry out programs. Devices that connect to the computer system are external peripherals, and examples include keyboards, mice, displays, printers, and external hard drives. These gadgets are for both data input into and data output from computers. For instance, a monitor and printer are output devices that display or print data from the computer, whereas a keyboard and mouse are input devices that enable the user to enter commands and data into the computer.
Other forms of computer hardware include graphics cards, hard disk drives, and solid-state drives. Graphics cards enhance the computer’s capability to show images and video. On the other hand, storage devices offer long-term storage capacity for data and applications. Additionally, there are many kinds of ports, connectors, and cables that enable communication between various components. In general, computer hardware is crucial to a computer’s ability to work and complete the tasks it needs to accomplish.
What are the absolute dos and don’t of building a PC?
The only surefire method to make sure that your system can accommodate all of your specific tastes is to build a gaming PC from the ground up. You can be sure that you’ll be able to play the games you want at the frame rates you desire when you choose everything that goes into your PC, starting with the power supply. A home-built PC also leaves room for improvements as technology advances, your preferences and needs change, or as your budget permits.
A good build needs careful attention to detail and adherence to a few dos and don’ts, but it can be a fun and gratifying experience. First off, before beginning the build, it is imperative that you perform extensive research and planning. It’s important to understand how components interact, so pick parts that are compatible, within your budget, and meet your performance needs. To avoid harming delicate electronic components, it’s also crucial to ground yourself correctly and work in an anti-static atmosphere. During the assembling procedure, following the manufacturer’s instructions and reviewing online resources can be of great assistance.
The adage “if it seems too good to be true, it probably is” is a good general rule to follow. Research should take up 80% of the time it takes to construct. The most complex and expensive component combination is RAM-CPU-Motherboard. A strong memory is necessary. It is crucial to note that it is extremely vulnerable to static electricity shocks. Be fearful of it. Do not touch any components or system units before touching another metal object, even if you are wearing a static discharge wristband.
Each month that Windows receives upgrades, its appetite for memory increases. Don’t forget to give yourself enough. The last thing you want six months after construction is to have to add extra memory (if you can prevent it). Virtual Memory equals Real Disk. Use your power supply sparingly. It’s not a nice thing to try to add a disk and discover that you’re out of power. If you multiply 600 watts by 7, then 750 watts by 1,000.
Conclusion
High-quality materials that can tolerate severe heat and are long-lasting are the best materials to make computer components. They are nevertheless still vulnerable to harm from internal as well as external sources, such as abuse or virus assaults. Knowing the five main parts of a computer will increase your understanding of how it works and make it simpler for you to spot potential problems. Unless you know certain tricks to boost your PC’s performance without reaching into your wallet, a hardware upgrade may be the best option if your computer starts to slow down after a few years.
However, there are a number of don’ts that must be scrupulously avoided when building a PC. First of all, never push parts into position. Before attempting to install something if it doesn’t fit, make sure it is compatible or that you are in the proper orientation. Avoid ignoring cable management, which is yet another essential don’t. Messy cables may hinder airflow, increase temperatures, and shorten the life and functionality of the system. When mounting the CPU cooler, remember to apply the thermal paste correctly since poor application can cause overheating problems. Finally, take your time when building. To avoid mistakes that can require more time and money to fix, take your time, be patient, and double-check each step as you go.





